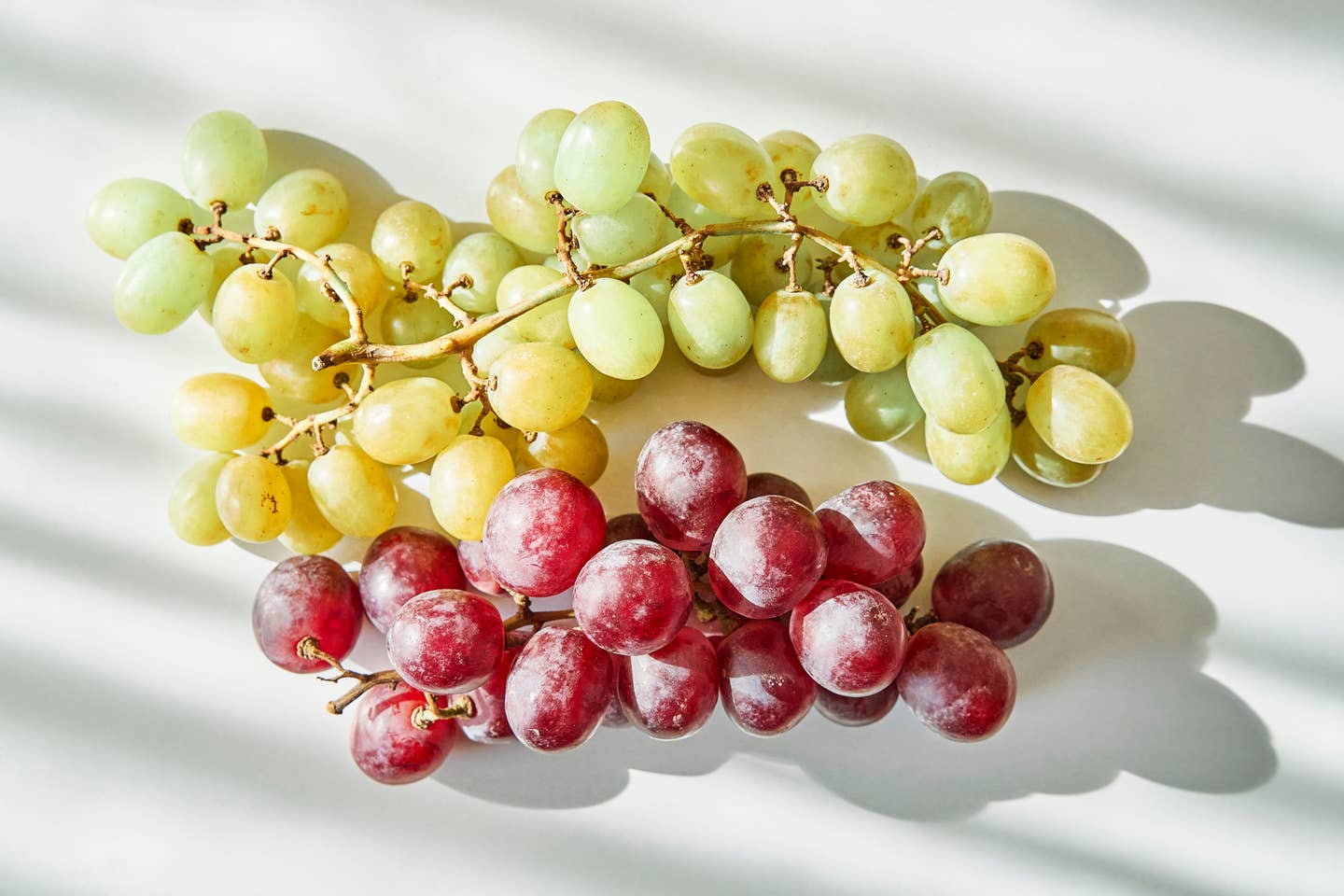
Eat This Fruit Daily to Stay Sharp and Live Longer, Research Finds
Eating grapes is potentially the cheapest, easiest way to improve your immune system, your metabolism, and your brain health. For around $2.09 per pound, grapes contain a bounty of essential nutrients including Vitamin C, antioxidants, calcium, and more. Now, three new studies suggest that just adding two cups of grapes to a high-fat diet can provide remarkable health benefits, surpassing our understanding of the benefits of grapes.
Dr. John Pezzuto examined the health benefits of grapes with a team of researchers from Western New England University. The three studies focus on lifespan, metabolism, fatty liver disease, and brain health, revealing that grape consumption yielded reductions in fatty liver and extended lifespans. To conduct the studies, the researchers analyzed how grape consumption altered gene expression in mice. Despite not conducting human tests, the researchers emphasize that these results can reliably translate to human health issues.
“We have all heard the saying ‘you are what you eat,' which is obviously true since we all start out as a fetus and end up being an adult by eating food,” Western New England University Researcher and senior author of three new studies Dr. John Pezzuto said. “But these studies add an entirely new dimension to that old saying. Not only is food converted to our body parts, but as shown by our work with dietary grapes, it actually changes our genetic expression. That is truly remarkable.”
First Study: Longevity and Fatty Liver Disease
Pezzuto’s first study concluded that grape consumption triggered unique gene expressions in the mice. This study found that grape consumption led to a reduced risk of fatty liver disease and expanded the overall lifespan of the animal consuming the grapes. To properly conduct the study, the animals followed a high-fat western style diet. Published in Foods, this study claims that grape consumption can modulate the adverse effects of a traditional Western diet, preventing oxidative damage.
“What is the effect of this alteration of gene expression? Fatty liver, which affects around 25% of the world’s population and can eventually lead to untoward effects, including liver cancer, is prevented or delayed,” the researchers stated. “The genes responsible for the development of fatty liver were altered in a beneficial way by feeding grapes.”
Second Study: Metabolism
The second study, published in Food & Function, found that the consumption of grapes changes metabolism. When Pezzuto and his research team introduced grapes to mice following high-fat diets, researchers found increased levels of antioxidant genes in the mice. The study concluded that grapes help reprogram the metabolism of the gut microbiota, increasing the efficiency of the liver and energy production.
“Many people think about taking dietary supplements that boast high antioxidant activity,” Pezzuto said. “In actual fact, though, you cannot consume enough of an antioxidant to make a big difference. But if you change the level of antioxidant gene expression, as we observed with grapes added to the diet, the result is a catalytic response that can make a real difference.”
Third Study: Brain Health
Published in the journal Antioxidants, the final study observed how grape consumption benefits brain function. The research highlights that a high-fat diet presents negative behavioral and cognitive pressures on the brain. In contrast, grape consumption helps alleviate these pressures, having a positive effect on the brain and brain metabolism. The researchers noted that this initial conclusion will require more research to determine the extent of the positive impacts.
“Although it is not an exact science to translate years of lifespan from a mouse to a human, our best estimate is the change observed in the study would correspond to an additional 4-5 years in the life of a human,” Pezzuto said. “Precisely how all of this relates to humans remains to be seen, but it is clear that the addition of grapes to the diet changes gene expression in more than the liver.”
Plant-Based Diet Improves Longevity
This February, a study found that a mostly plant-based diet can prolong life expectancy by over 10 years. The team of Norweigan researchers found that introducing more plant-based foods earlier in life helps cut down the risk of life-threatening disease and improves your overall health. Following an "optimal" diet – defined as primarily plant-based a little fish – showed long-term health benefits, whereas diets high in red or processed meat showed an inverse relationship.
Another study from last March found that eating more plant-based is key to maintaining a healthy gut. This study concluded that by improving gut health, you can improve longevity and prolong your lifespan. The researchers claim that building a healthy microbiome at an earlier age is essential to better health in old age.
For more plant-based happenings, visit The Beet's News articles.
The 13 Best Foods to Boost Your Immune System to Fight Off COVID-19 Symptoms
Here are the best foods to eat on repeat, to boost immunity and fight inflammation. And stay off the red meat.
1. Citrus for Your Cells and Healing
Your body does not produce vitamin C, which means you need to get it daily to have enough to create healthy collagen (the building blocks for your skin and healing).The recommended daily amount to shoot for is 65 to 90 milligrams a day, which is the equivalent of one small glass of orange juice or eating a whole grapefruit. Almost all citrus fruits are high in vitamin C. With such a variety to choose from, it's easy to get your fill.
2. Red Peppers to Pump Up Skin and Boost Immunity with Twice the Amount of Vitamin C as an Orange Has
Want even more vitamin C, add red bell peppers to your salad or pasta sauce. One medium-sized red bell pepper contains 152 milligrams of vitamin C, or enough to fulfill your RDA. Peppers are also a great source of beta carotene, a precursor of vitamin A (retinol). How much beta carotene do you need a day: You should try to get 75 to 180 micrograms a day which is the equivalent of one medium bell pepper a day. But a red pepper has more than two and a half times your RDA for vitamin C so eat them all winter long.
3. Broccoli, But Eat It Nearly Raw, to get the Most Nutrients Out of It!
Broccoli may be the most super of superfoods on the planet. It's rich in vitamins A and C as well as E. The phytochemicals in it are great for arming and strengthening your immune system.How much lutein should you eat in a day: There is no RDA for lutein, but experts say get at least 6 milligrams.
4. Garlic, Eaten By the Clove
Garlic isn't just a great flavor-enhancer, it's essential for your health. Garlic’s immune-boosting properties are tied to its sulfur-containing compounds, such as allicin. Allicin is thought to improve your immune cells' ability to fight off colds and flu, and viruses of all kinds. (Smelling more garlic on the subway? It could be smart coronavirus management.) Garlic also has anti-microbial and anti-viral properties thought to fight off infections. How much should you eat in a day: The optimal amount of garlic to eat is more than most of us can fathom: Two to three cloves a day. While that may not be doable, realistically, some people take garlic supplements to get 300-mg dried garlic in a powdered tablet.
5. Ginger is a Power Player for Immunity and Digestion
Ginger is another ingredient that has super properties when it comes to fighting off illness. It has been shown to decrease inflammation, which can help if you get swollen glands or a sore throat or any inflammatory ailment. Gingerol, the main bioactive compound in ginger, is a relative of capsaicin, and is responsible for much of its medicinal properties. It has powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits.How much should you eat a day: Most recommendations land on 3–4 grams of ginger extract a day, or up to four cups of ginger tea, but no more than 1 gram a day if you are pregnant. Some studies have linked high dosages to an increased risk of miscarriage.
6. Spinach, Wilted, Not Steamed (Also Kale and Dark Leafy Greens of All Kinds)
Spinach is not only packed with vitamin C but also antioxidants and beta carotene, both of which give your immune system the healthy boost it needs to fight off invaders. Don't overcook your spinach, since the more it's cooked the less active the antioxidants will be. If you eat it raw or lightly steamed you'll keep more of the nutrients intact.How much should you eat a day: Aim for 1 cup fresh spinach or 1/2 cup cooked per day, but this is the right moment to try the raw or slightly wilted approach. Order warm or wilted spinach salad when you go out, or make it yourself with olive oil, pine nuts, and vegan parm.
7. Almonds for the Win, Pop Them Like Candy
Vitamin E in almonds will help ward off colds and flu and is key to your immune system humming along. It’s a fat-soluble molecule, meaning it requires the presence of fat to be absorbed, so nuts are the perfect package for E to make it into your system.How much should you eat in a day: A half-cup serving, or 46 whole, shelled almonds, provides almost 100 percent of your RDA of vitamin E. Almonds are great for you but they don't come with a "free" pass, since 1/4 cup is a serving and has 162 calories, so double that for your RDA and you're eating about 325 calories. Throw them into smoothies instead.
8. Turmeric to Fight Inflammation, Put it In Your Tea or Smoothie
This highly pigmented spice is known for its anti-inflammatory qualities. How it helps immunity? It decreases exercise-induced muscle damage. Tumeric bolsters the immune system by stimulating antibody formation and people with auto-immune diseases are told by their doctors to take 500 mg of curcumin daily to reduce inflammation and stave off soreness.How much should you eat in a day: Try adding extra Tumeric to your diet during periods of stress or during flu season. Or take 500-2,000 mg of curcumin to help fight inflammation and power up your immune system.
9. Green Tea by the Gallon, Skip the Coffee and Sip this Instead
Green tea has high levels of EGCG, (epigallocatechin gallate) a hard-working antioxidant that is known to boost immune function. Green tea is steamed so the EGCG is still active when you drink it.Green tea also contains L-theanine, an anti-oxidant which appears to help in the production of T-cells in your body, the killer L-theanine may aid in the production of germ-fighting compounds in your T-cells.How much green tea should you drink in a day: The optimal amount is three to five cups in a day, but most people won't get to that level. Any amount is better than nothing. Swap out a usual beverage daily for green tea could improve your health.
10. Papaya, The Tropical Healer to Keep You Vacation-Healthy All Year Round
Papaya delivers over twice your recommended daily amount of vitamin C in one fruit. It also contains an enzyme called papain that has anti-inflammatory effects -- and inflammation is one factor in most illnesses, so avoiding it can help your body fight off bacterial infections like sinusitis.Papayas contain potassium, vitamin B, and folate, which is a powerful cell rebuilder. Exactly how folic acid works to build immunity is linked to its role in protein synthesis, and researchers think that any mechanism in which cells proliferate can be affected (which is why it's critical for pregnant women). People who are folate-deficient have compromised immune systems.How much folate should you eat a day: Whether you are pregnant or not, folate (vitamin B9) is a great vitamin to keep your cells healthy and strong. The recommendation is 400 micrograms a day, or get it from legumes, spinach, papayas, and avocados.
11. Kiwis, a Vitamin Powerhouse
Kiwis are full of folate, vitamin K, vitamin C, and potassium. These vitamins in combination work in the body to build healthy cells, fight infection and keep your immune system humming along. Vitamin K deficiency is rare but when people don't have enough they suffer from weak bones and compromised immune systems. The inflammation system in the body is also dependent on vitamin K, especially your killer T cells that mobilize and fight cancer and other diseases.How much should you eat in a day: Vitamin K is one of the unsung heroes of the body. Women should get 90 micrograms a day, and men should have 120 micrograms.
12. Sunflower seeds to sprinkle on salads or eat by themselves
Sunflower seeds are especially healthy since they provide phosphorus, magnesium and vitamin B-6 as well as vitamin E. Your immune system needs vitamin E to function at full throttle. You can also get vitamin E from avocados and spinach and broccoli.How much should you eat in a day: Anywhere from 1 ounce (30 grams) per day to a healthy handful is considered healthy, but because they are high in sodium you might want to refrain from eating the entire bag. The raw seeds have 204 calories per quarter cup.
13. Miso, Soup or Paste to Add to Your Soups and Salad Dressings
The nutrients in miso -- which is a soybean paste that has been fermented with salt and a koji starter -- boosts immune system function by delivering healthy probiotics to the gut, making your microbiome healthier. How does Miso benefit your immune system? It is a "sirt" food, which are foods that contain high levels of ‘sirtuins’ or proteins that regulate cells and activate metabolism. A diet high in sirts is believed to lead to weight loss, increased wellness and longevity.How much should you eat in a day? Researchers believe that consuming one bowl of miso soup per day, as is the tradition in Japan, lowers the risks of breast cancer. Other than its high sodium content there is no reason to stay away from miso with all its varied health benefits. We say cheers to that.
More From The Beet