The 10 Best Anti-Inflammatory Foods You Should Be Eating Right Now
Inflammation is a process that helps your body fight off infections, heal injuries, and flush out toxins. While it is beneficial to ward off things that are harmful, inflammation that persists can be dangerous and "chronic inflammation" can negatively influence blood flow, harming cell tissue, and organs. It is a culprit in heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, stroke, and is known as a risk factor for serious symptoms of COVID-19. Research shows that it is linked to chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Diet and lifestyle changes are key to reducing chronic inflammationy. Some healthy steps you can take to decrease inflammation are getting daily exercise, reducing stress, and getting quality sleep, regularly. One of the most powerful tools to protect against chronic inflammation is to eat a diet rich in plant-based whole foods, experts say. “Making good choices in our diet to include fresh vegetables and fruits as well as reducing refined sugar intake can make a big difference," said Dr. Varinthrej Pitis, MD, an internal medicine physician at Scripps Clinic in Carmel Valley in a Scripps article.
Studies have shown the link between the role of a whole-foods, plant-based diet in reducing chronic inflammation: A 2019 study published in Nutrients found a relationship between the Meditteranean diet and cancer incidence, demonstrating that the key nutrients in the diet help can fight chronic inflammatory cells. Another 2019 study published in Nutrition and Aging found that an anti-inflammatory diet can reduce the force of neuroinflammation, resulting in a lower likelihood of Alzheimer’s disease.
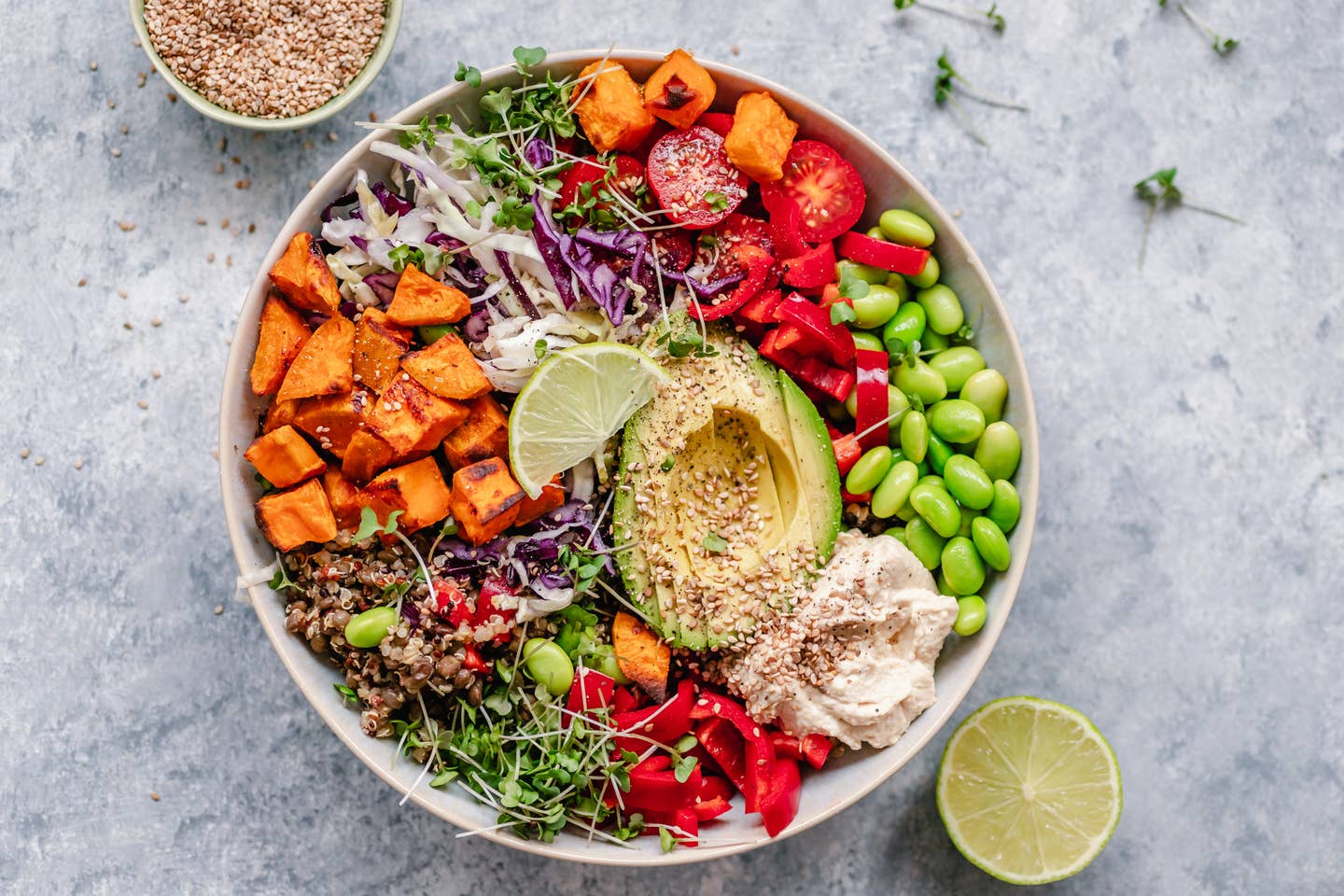
Below are the top 10 plant-based foods that will fight inflammation and nourish your body.
10 Plant-Based Foods to Fight Inflammation
1. Avocados
This popular toast pairing is packed with potassium, magnesium, fiber, and healthy fats. A 2020 study found that avocado is beneficial in reducing obesity, which activates low-grade inflammation and oxidative stress. The study found that avocados “induce antioxidant and anti‐inflammatory effects by improving enzymatic activity and modulating obesity‐related impairments in the anti‐inflammatory system in different tissues, without side effects.”
2. Berries
This colorful fruit is filled with tons of antioxidants that can reduce your risk of disease. A 2017 study published in Molecules examined the healthy properties of berries, finding that they are neuroprotective, meaning that they protect nerve cells from further damage. This effect may be linked to lower toxicity and inflammation, which are associated with chronic diseases.
3. Cocoa
Cocoa is a powder of ground cacao beans, heavily concentrated in dark chocolate. Cocoa contains flavanols that reduce your body’s oxidative stress, according to a 2019 study published in Nutrients. Oxidative stress is when there is an imbalance of free radicals and antioxidants in the body. High levels of oxidative stress can cause chronic inflammation, leading to damaged cells, proteins, and DNA in the body.
4. Extra virgin olive oil
This Mediterranean diet staple is a healthy fat-filled with nutritious benefits. A 2019 study published in Nutrients found that extra virgin olive oil contains polyphenols that decrease the amount of inflammatory markers in the body. The study also suggests that it is an important dietary tool in preventing chronic diseases like obesity.
5. Grapes
This popular fruit has important nutrients like vitamin K, copper, and manganese. It is also a great source of resveratrol, a key compound that has been found to prevent and mitigate intestinal inflammation, according to a 2017 study published in Nutrition Research Reviews. This could alleviate symptoms with chronic gastrointestinal diseases like IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) and perianal infections.
6. Green tea
Green tea is made from the camellia Sinensis plant filled with tons of antioxidants. A 2017 study published in Nutrients found that this tea contains polyphenols such as epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which reduces the surge of inflammatory markers like cytokines. This research shows that green tea can be used as diet therapy to relieve symptoms and prevent inflammation.
7. Mushrooms
This soft vegetable is low in calories and is a great source of selenium, copper, and B vitamins. A 2018 study found that reishi mushrooms protected against gut inflammation due to a reduction in the inflammatory cytokines. This vegetable could be incredibly helpful for people with sepsis, a condition caused by the body’s response to infection.
8. Peppers
Peppers are loaded with high amounts of vitamin C, similar to what is found in citrus fruits. They are filled with capsaicin, which has anti-inflammatory properties, according to a 2017 study published in Pharmacognosy Magazine. The study found that the consumption of capsaicin-rich foods, such as chili peppers, can reduce the inflammatory effects in muscle-related diseases such as myotube atrophy.
9. Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a great source of vitamin C, potassium, and folate. They also are a major dietary source of the antioxidant lycopene, which has been shown to reduce pro-inflammatory compounds causing heart disease, according to a 2017 study. This has been linked to many health benefits, such as a low risk of contracting cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
10. Turmeric
Turmeric is a spice-filled with curcumin, a nutrient known for its many health benefits. A 2018 study published in The Journal of Immunology found that curcumin in turmeric inhibits inflammation through suppressing the pathways that active it in the body. This points to the potential use of turmeric as a herbal supplement in helping alleviate symptoms with inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
More From The Beet