What Is Soy Protein Isolate, Found In Vegan Food, and Is It Bad For You?
You see this ingredient in so many vegan products, but what is it? And should you be worried about eating it? Here is the scoop on Soy Protein Isolate and why it's in so many vegan or plant-based foods.
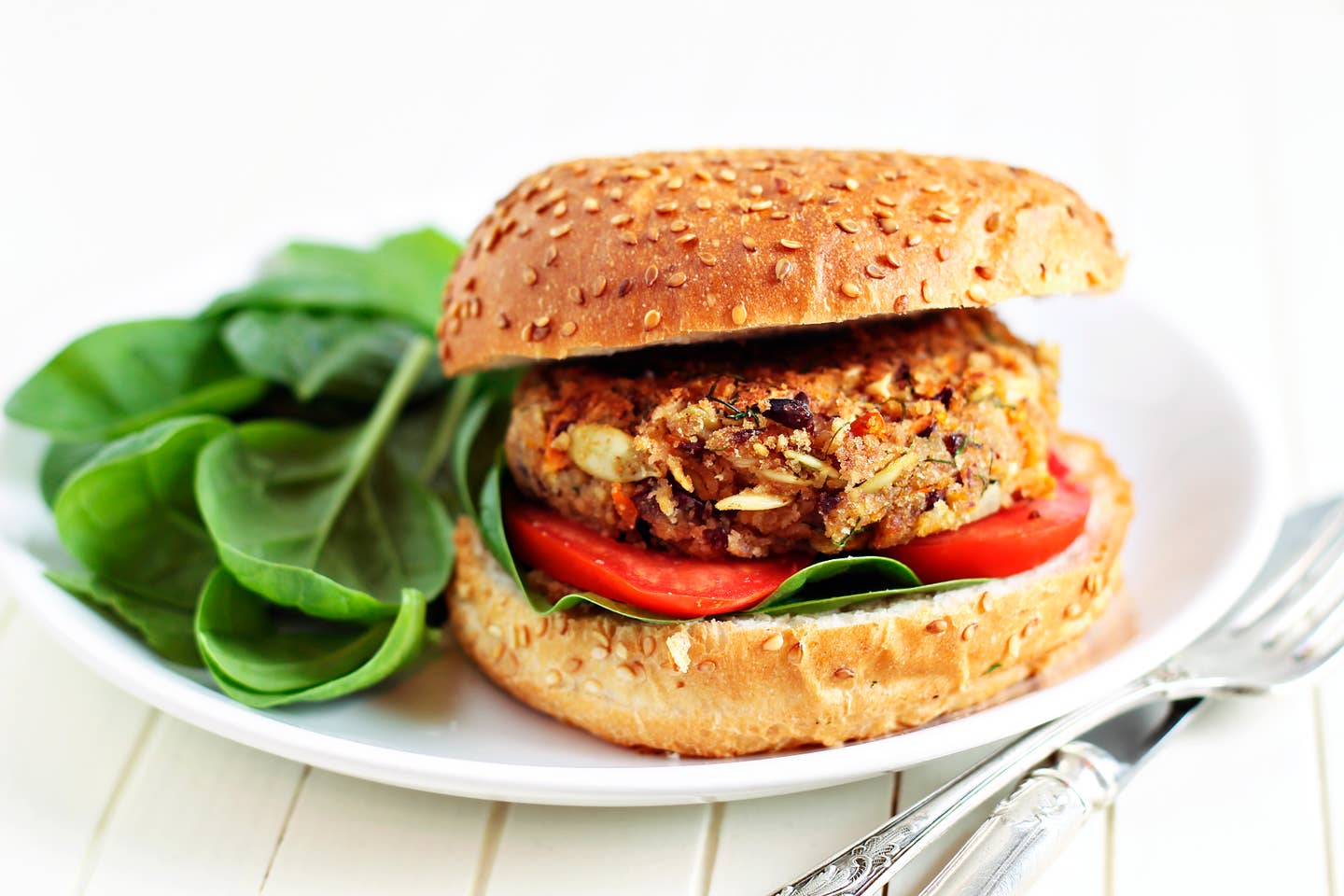
The Impossible Burger has it. So, too, do vegan protein bars, other fake meats, and some granolas. In fact, suffice to say that if you’re eating vegan food, you’re probably consuming soy protein isolate. Yet while you’re familiar with soy and protein and know they’re healthy, the isolate part has you confused. No more, as experts weigh in below and explain what this foreign-sounding ingredient is–and why it shouldn’t actually be a huge worry.
Defining what is soy protein isolate?
True to its name, soy protein isolate originates from soy, specifically defatted and dehulled soybeans, according to the Journal of Nutrition. By soaking the soybeans, protein can essentially be isolated out and dehydrated. As a result, that soy protein isolate becomes an ultra-rich source of protein, its content about 90 percent protein, says Nanci S. Guest, Ph.D., R.D., C.S.C.S., plant-based dietitian and nutrition scientist at the University of Toronto in Ontario.
Soy protein isolate is then added to foods, which not only boosts the protein content but also does so without adding additional fat or calories. It’s not unlike how manufacturers use whey protein isolate with one obvious difference. “Soy protein isolate is from plants, and whey is one of two proteins from dairy,” Guest says.
The pros and cons of soy protein isolate
Throughout the years, soy has had to fight to earn its justly deserved spot in the health food world, people often harboring an erroneous belief that isoflavones, also called phytoestrogens, in soy can increase your risk of breast or prostate (or other hormonal) cancer. Fortunately, numerous studies now exist to show the benefits of eating a moderate amount of whole soy foods like soybeans and edamame, and even minimally processed soy foods like tofu and soy milk. “These foods help reduce the risk of cancer, especially breast and hormone-related cancers, and recurrence of cancer,” says Susan Levin, M.S., R.D., C.S.S.D., director of nutrition education for the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine.
So what’s the worry with soy protein isolate? There’s some concern that like cow’s milk, soy protein isolate may increase insulin-like growth factors such as IGF-1. “Once soy protein isolate is extracted from food, it may promote cancer and cancer growth,” Levin says, citing a study in Nutrition and Cancer that recommended men with early-stage prostate cancer "not to exceed dietary protein recommendations."
Others, however, say otherwise. “There’s zero evidence that soy protein isolate acts differently than soy food,” Guest says. In fact, soy protein isolate may actually have some health benefits.
Soy protein isolate may be beneficial in small amounts
According to the National Cancer Institute (NCI), soy protein isolate has been shown to “reduce tumor incidence and growth in some animal studies and may also “inhibit endothelial cell proliferation.” And because it does contain phytoestrogens, displaying mild estrogen-like effects as a result, soy protein isolate may help regulate hormone balance and reduce the risks of breast cancer, heart disease and osteoporosis. Levin notes, however, that the NCI is citing studies done on animals, not humans, which could affect results.
And for individuals who are wanting to make fitness gains in the gym, soy protein isolate might be beneficial there as well:” Soy protein isolate is firmly established as a high-quality protein that promotes gains in muscle mass and strength among individuals engaged in resistance exercise training,” says Mark Messina, Ph,D., M.S., president of Nutrition Matters in Pittsfield, Mass. Soy protein isolate also lowers cholesterol modestly.
Should you eat soy protein isolate if you want to get more protein in your diet?
Whether you eat soy protein isolate depends on what you’re hoping to get from it. If you want to receive all of the same health-promoting benefits as whole soy foods, you might be out of luck. “Soy protein isolate is lower in isoflavones and doesn’t provide some of the other components found in whole soy like fiber and omega-3 fatty acids,” says Messina, although he does say that both soy foods and isolate can have a role in the diet.
On the flip side, though, soy protein isolate can help you meet your protein needs. The question, of course, becomes whether you need that much protein in a single serving. “A small food item with 20 grams of protein is a ridiculously high amount,” Levin says, adding that it may be more of a marketing ploy at this point. “Companies are playing on your fear that you need more protein.”
In the end, soy protein isolate isn’t the biggest red flag in the health world, and if you eat it every now and then or in moderation, it shouldn’t be a concern, Levin says. Yet for optimal benefits, strive to eat whole sources of soy whenever possible.
More From The Beet