Vegan Fast-Food Options Saved 600,000 Animal Lives in 2021
2021 marked a year of impressive and unlikely innovations within the plant-based world. From 3D printed vegan meat to strides in cell-based meat production, the alternative protein market is flourishing. But the most shocking development is that fast-food giants have turned a significant corner, adopting plant-based menu items and initiating companywide sustainability campaigns. Plant-based fast food help save the lives of more than 630,000 animals in 2021 as meatless options become standard practice for the industry.
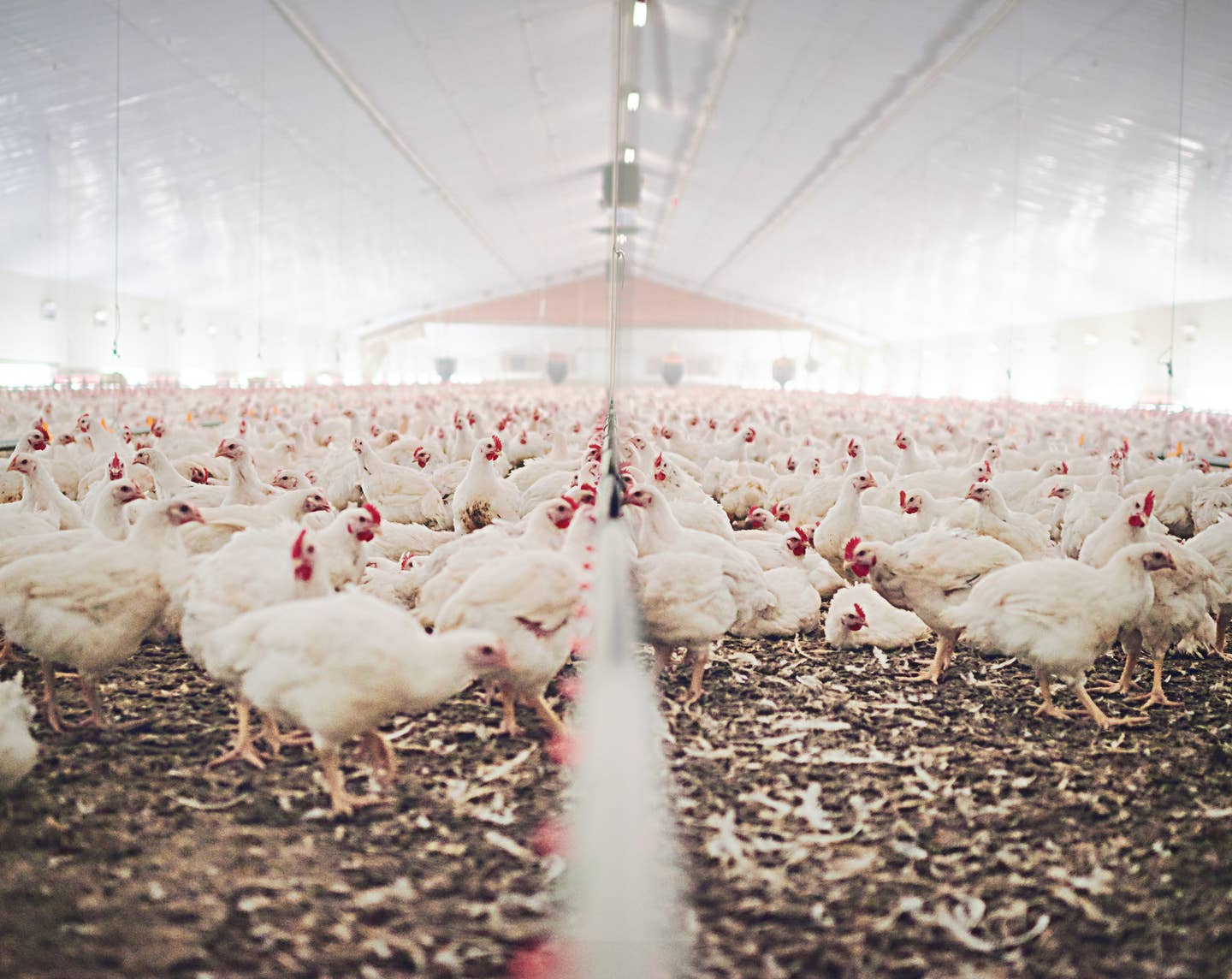
Animal-rights organization World Animal Protection (WAP) just released a report that claims 630,000 animals were saved from the food system in the United States. The report indicates that the animals saved can be directly attributed to the increase in vegan fast-food options and growing consumer interest in plant-based meat.
"Restaurants are definitely trying to meet this rising demand for plant-based products by offering more meat alternatives on their menus," Farming Campaign Manager at World Animal Protection Maha Bazzi said to USA TODAY. "The industry is expected to stay the course in 2022 as meat alternatives evolve and become more widely accessible."
The WAP report detailed that approximately 211,000 pigs, 35,000 chickens, and 77,000 cows were removed from the food system last year. The organization used data from Carl’s Jr. which revealed the company's locations consistently sold 30 Beyond burgers every day since its release. The information was then applied to sales data that assumed that people were not eating more fast food but instead substituting meat-based orders with vegan alternatives.
The data follows the most successful year for plant-based distribution within the fast-food market. Several fast-food giants debuted new plant-based menu options. Overall, vegan meat is featured on menus 1320 percent more since the start of the pandemic. By rolling out new vegan items nationally, fast food is helping to make plant-based protein more accessible than ever before. McDonald’s – the biggest fast-food corporation on the planet – successfully launched its vegan McPlant burger last year, which is now available at 300 locations.
Alongside McDonald’s, other fast-food giants including KFC and Panda Express have developed plant-based alternatives to some of its most popular menu selections. KFC recently launched its Beyond Chicken Tenders made with Beyond Meat to approximately 4,000 locations nationwide. Panda Express first entered the plant-based protein market when it debuted its Beyond The Original Orange Chicken. Following the widespread positive response, the quick service American-Chinese restaurant began to test two new plant-based menu items: Mapo Tofu with Beyond Beef and String Beans with Beyond Beef.
Impossible Foods also increased its fast-food presence. The company launched Impossible Chicken Nuggets at Burger King to accompany the popular Impossible Whopper. The increased presence of plant-based protein is fueling a rapidly growing vegan fast food market. The vegan fast-food market is expected to reach $40 billion by 2028, increasing at an unprecedented 11.4 percent growth rate.
"Looking ahead to 2022, we know that in this category, it’s not enough to just have any plant-based product in the market now. You have to prove to people that you have better products," Impossible Foods President Dennis Woodside told USA TODAY. "We did that last year with our Impossible Chicken Nuggets, Impossible Pork, and Impossible Sausage products – all of which were found by the majority of consumers to be as good as or better than the respective animal-based products in recent taste tests."
Nearly 90 percent of plant-based meat purchases come from non-vegans, according to research data. By increasing accessibility to plant-based meat, fast food chains have brought plant-based foods to people who would most likely purchase meat. Over the last year, the data shows that with increased availability of meat alternatives consumers are more likely to reduce meat consumption, saving animals and reducing harmful environmental impacts from animal agriculture.
Fast-food restaurants have finally got the memo that their customer base isn’t just coming through for a burger, fried chicken, or a beef taco. Many now have plant-based foods and are coming up with creative, delicious ways to get more greens on the menu. Here are the 6 best fast-food chains with plant-based options on the menu.
1. Burger King
Turns out there’s a lot more to rely on than a salad if you’re eating plant-based. Burger King has the Impossible Whopper featuring a meatless patty as well as a few secretly vegan options such as the French Toast Sticks and Hashbrowns.
2. White Castle
Known for its mini square-shaped sliders, this hamburger chain jumped on the plant-based bandwagon at some participating locations. You can find an Impossible Slider on some White Castle menus.
3. Del Taco
This was the first national Mexican fast-food chain to offer Beyond Meat at the company’s 580 restaurants across the country. Del Taco has the Beyond Avocado Taco on the menu along with the Epic Beyond Original Mex Burrito and Avocado Veggie Bowl.
4. Carl's Jr.
Another brand synonymous with beef burgers, Carl’s Jr. offers several plant-based options for veggie and plant lover such as Beyond Famous Star Burger and Guacamole Thickburger.
5. Taco Bell
This fast-food restaurant may have been one of the first you frequented while transitioning to plant-based eating. That’s because Taco Bell has eight million vegetarian combinations and sells 350 million vegetarian items a year through menu substitutions or ordering off their vegetarian menu. In fact, they were the first quick-service restaurant to offer American Vegetarian Association (AVA) certified food options.
6. Starbucks
From the time it started offering breakfast sandwiches in 2006, the coffee conglomerate became a competitor in the fast-food space. You can get your favorite hot and cold beverages made with almond, coconut or oat milk but there are also plant-based food options available such as the Baja Black Bean Veggie Wrap, bagel with vegan cream cheese and Impossible Breakfast Sandwich.
More From The Beet