8 Countries Pledge to Cut Methane Emissions 30 Percent by 2030
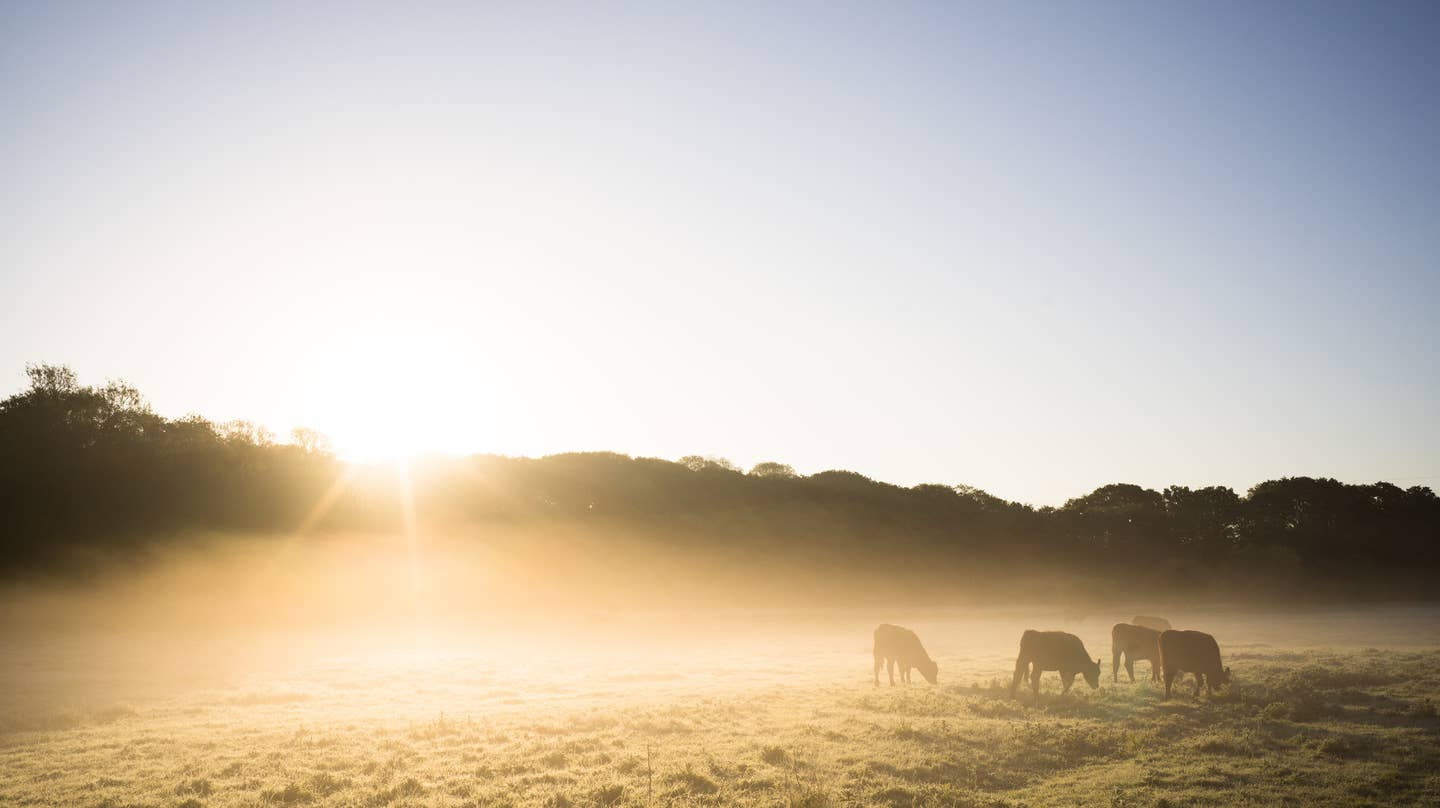
As climate change activists narrow in on the animal agricultural industry, governments worldwide are initiating programs to cut down emissions across the entire market. Recently, eight countries announced pledges to reduce methane emissions by 30 percent over the next ten years. The United States and European Union just announced the Global Methane Pledge to reduce worldwide methane emissions ahead of the UN Climate Change Conference (COP26) this year.
The announcement follows the UN’s “code red” report that called for immediate regulations restricting the level of greenhouse gas emissions worldwide. Following this research, the European Commission declared that reducing methane emissions, across every industry, is the “single most effective strategy in reducing global warming."
The environmentalist pledge was introduced during a virtual conference regarding the climate crisis that hosted world leaders to discuss future regulatory measures. The involved countries include Argentina, Indonesia, Italy, Mexico, the UK, Ghana, Iraq, and the United States. The European Union also joined the discussions. The White House revealed in a statement that among the enlisted countries, six of the top 15 methane emitters were represented.
“This will not only rapidly reduce the rate of global warming, but it will also produce a very valuable side benefit, like improving public health and agricultural output,” President Joseph Biden said. “We believe the collective goal is both ambitious but realistic. And we urge you to join us in announcing this pledge at COP26.
The countries signing the pledge promise to cut emissions by 2030. The EU Commission announced that if all participating countries follow these regulations that it could limit global warming by 0.2 degrees celsius by 2050.
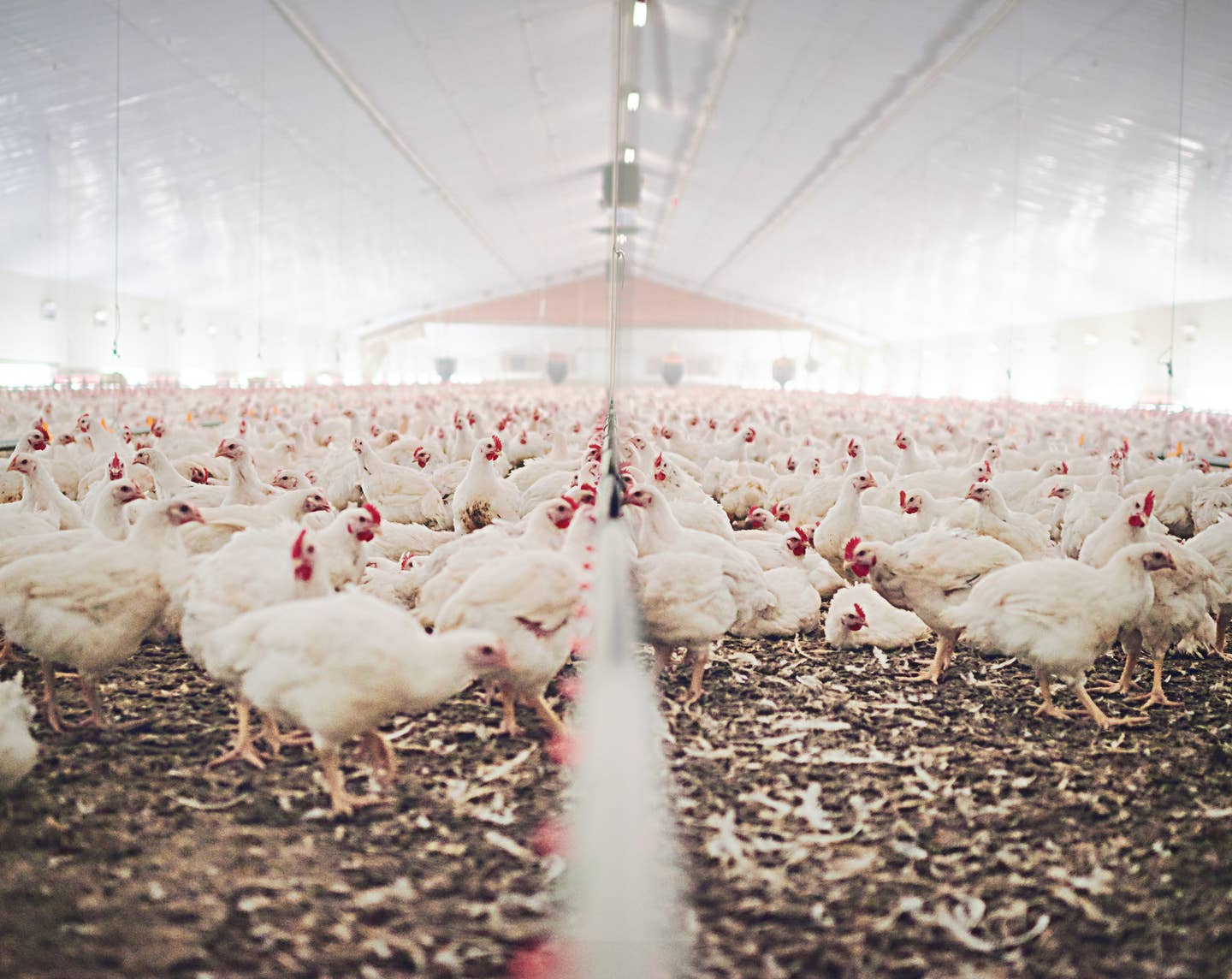
According to the United States Department of Agriculture, 10 percent of US greenhouse gas emissions can be traced to the agriculture industry, specifically through livestock production. The USDA reports that methane comprises 36 percent of greenhouse gases produced in the entire agriculture industry. The pledge argues that cutting the methane emissions worldwide could slow the human impact on the climate crisis and move towards reversal.
President Biden believes that by working with the other countries, the global animal agriculture industry could innovate its current production practices to incorporate more sustainable technologies. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the world will tackle the environmentally damaging byproducts of the animal agriculture industry. Beyond the animal agriculture industry, the pledge promises to extend its regulations across multiple areas including the energy sector and pollution.
“Countries have widely varying methane emissions profiles and reduction potential, but all can contribute to achieving the collective global goal through additional domestic methane reduction and international cooperative actions,” the Joint US-EU statement reads. “Major sources of methane emissions include oil and gas, coal, agriculture, and landfills.”
The United Nations recently released its Global Methane Assessment: Benefits and Costs of Mitigating Methane Emissions report that explained the impact that the highly volatile greenhouse gas had on the environment. The report highlights the human causes that have increased methane emissions over the recent decades, emphasizing the need to reduce its emissions as it is ten times more powerful than C02 when regarding climate warming.
“The existence of readily available, low-cost, targeted measures, and methane’s short-lived atmospheric lifetime means significant climate and clean air benefits can be achieved by 2030.” the report reads. “Targets and performance indicators to reduce methane must address the combined and multiple impacts methane has on climate, air quality, public health, agricultural production, and ecosystem health.”
20 Athletes Who Went Vegan to Get Stronger
1. Novak Djokovic: Number one tennis champion in the world
The number one tennis player in the world, Novak Djokovic, went plant-based more than twelve years ago to enhance his athletic performance and win more matches. In recent interviews, he has credited going vegan with helping him rise from third place in the world to first in the world because it helped clear his allergies. Before changing his diet, Djokovic had searched for cures to the breathing issues that cost him matches and focus which caused him to struggled during his most intense matches. The allergies used to make him feel like he couldn’t breathe and would be forced to retire from competitive matches as he did in Australia. "Eating meat was hard on my digestion and that took a lot of essential energy that I need for my focus, for recovery, for the next training session, and for the next match," he said. Djokovic emphasized he does not eat foods that require a lot of digestion, especially in the morning, when he needs all of his energy for training. Instead, he starts the day with hot water and lemon, then celery juice, and some superfood supplements.
2. Tia Blanco: Professional Surfer and Beyond Meat Ambassador Read More: 20 Who Athletes Swear by a Plant-Based Diet to Boost Performance
Tia Blanco won gold at the International Surfing Association Open in 2015 and credits her success to her vegan diet. Blanco reports that a vegan diet helps her stay strong and she enjoys eating different forms of vegan protein like nuts, seeds, beans, and legumes. The professional surfer was influenced by her mother, who is a vegetarian and grew up in a veggie-forward household, Blanco has never eaten meat in her life, which made the plant-based switch much easier. And speaking of making things easier, Blanco has an Instagram cooking page called @tiasvegankitchen where she shares her favorite simple vegan recipes so all of her fans can eat like their favorite professional vegan athlete. In addition to her home-cooked meals, Blanco recently became an ambassador for vegan company Beyond Meat and now she posts Instagram stories and highlights of her favorite meatless meat recipes.
3. Steph Davis: World Leading Professional Rock Climber
Steph Davis has been vegan for 18 years now and says, "there’s nothing in my life that hasn’t become better as a result, from climbing and athletics to mental and spiritual well being." Davis has competed on some of the most challenging verticle routes on the planet –like Concepcion (5.13), which is known to be one of the hardest pure climbs anywhere. Davis holds the third overall ascent and is the first female to ever make the ascent of the route. Davis described it as her "most technically demanding climb ever." Davis explained why she went vegan eight years ago when she partnered with PETA. "What can we do to start making changes in a positive way? And if it just so happens that changing our lifestyle leads to environmental benefits, health benefits, economic benefits, and positive social change, then all the better. One thing I’ve learned is you don’t have to do or be anything you don’t want to be, and you can change anything in your life just by starting to do it. It’s you who chooses who and what you are, by the things you think and the things you do." She goes on to add, "no one says you have to become a “perfect” vegan overnight. But why not start making small changes and see how it feels? I believe it’s the small choices people make that have the biggest power to change, and nothing is more simple yet also more far-reaching than changing how and what you choose to eat. We’re all here for a short time, in the end, and living a well-intentioned and compassionate life seems like what ultimately matters the most, the only real goal that I aspire to."
4. Venus Williams: Tennis Great
Tennis champion Venus Williams swears that making the switch to veganism was one of the factors that helped to improve her performance and get over an auto-immune disease. The tennis star went vegan back in 2011 when she was diagnosed with Sjögren's syndrome, a debilitating autoimmune disease with a range of symptoms from joint pain to swelling, numbness, burning eyes, digestive problems, and fatigue. She chose to eat plant-based to recover to her formerly healthy self, and it worked so she stuck to it. The seven-time Grand Slam singles champion recovers faster on a plant-based diet now, compared to how she felt back when she ate animal protein. When you have an auto-immune disease you often feel extreme fatigue and random body aches and for Venus, a plant-based diet provides energy and helps her reduce inflammation. The Beet reported on Willaim's diet and what she normally eats in a day to stay healthy, fit, and win more matches. Talking about her favorite dinner meal, Williams adds, “sometimes a girl just needs a donut!"
5. Mike Tyson: The First Heavyweight Boxer to Hold the WBA, WBC, and IBF Titles
Mike Tyson recently said he is "in the best shape ever" thanks to his vegan diet. The boxing legend then announced he's getting back into the rings after 15 years, to fight against Roy Jones, Jr. in California later this fall. Tyson went vegan ten years ago after dealing with health complications and in the wake of having cleaned up his life: “I was so congested from all the drugs and bad cocaine, I could hardly breathe." Tyson said, “I had high blood pressure, was almost dying, and had arthritis." Now, the 53-year-old powerhouse is sober, healthy, and fit. "Turning vegan helped me eliminate all those problems in my life,” and "I'm in the best shape ever." His new trainer agrees: Watching Iron Mike's speed during recent training sessions, observed: "He has the same power as a guy who is 21, 22-years old."
6. Chris Paul: The NBA's Newest Vegan Who Was Influenced by The Game Changers
Oklahoma City's point guard Chris Paul decided to ditch meat and dairy and was asked join on as a co-executive producer for the popular documentary, The Game Changers. For breakfast, Paul enjoys oatmeal with plant-based milk and nut butter. For lunch, he fuels up with pasta or brown rice with Beyond Meat sausage, grilled vegetables, and a curry sauce. His chef told USA Today, "The main thing is, we try to keep it as light and clean as possible for his normal routine, with organic ingredients. Anything that can minimize body inflammation. Chris is always worrying about what he can and can't eat." So far it appears he's getting it right. In an exclusive interview with The Beet's Awesome Vegans columnist Elysabeth Alfano, Paul said eating a plant-based diet helps him keep up with players half his age.
7. Colin Kaepernick: Former (future?) NFL Player and Social Activist
In 2016, Kaepernick made the switch to veganism with his longtime girlfriend to recover from a series of injuries that had him down for the count. The Beet recently reported on how this dietary switch has allowed Kaepernick to stay strong and healthy. Now, he's in the gym building muscle and looks fitter than ever. But will he be picked up? The professional football player claims that a vegan diet makes him feel "always ready" to perform his best on the field.
8. Cam Newton: New England Patriots' Newest Quarterback is Vegan
Cam Newton just replaced Tom Brady, who also follows a mostly plant-based diet, as the New England Patriot's QB, after having made the plant-based switch back in March 2019. The NFL Star first decided to ditch meat and dairy to recover quicker from injuries when he learned that a plant-based diet is proven to help reduce inflammation. "I've seen such a remarkable change in the way my body responds to the food that I eat," Newton told PETA for his recent partnership for a new campaign called, "Built Like a Vegan," proving that you don't need to eat meat to be strong. Newton enjoys a meat-free burger on a pretzel bun, heavy on pickles and sauce. He adds: "People often ask, 'How do you get your protein?' I just say, 'I get it in the same way you do, but it's fresher and cleaner.' " Newton shares how to do it: "My advice to a person who wants to become vegan is to eat on schedule. If you can eat on a schedule, you won't miss [a meal or crave meat] or think anything different, and you'll be alright."
9. Elijah Hall: American Sprinter Training for The 2021 Tokyo Olympics
Elijah Hall says about his vegan diet: "Going vegan was the best decision" he has ever made. Hall holds records in the indoor 200 meters and was training for the Tokyo this summer when it got postponed by a year due to the pandemic. Hall said "the effects that it’s having on my body are amazing. Becoming a plant-based athlete has opened many doors to my health and my training." We predict he'll only get faster in the next 11 months and break records, come home with golf and be the world champion in 12 months.
10. Morgan Mitchell: Omplyian Sprinter Who Won her First Title at 2014 Australian National Championships
Five-years ago, Morgan Mitchell went vegan and it made her faster, leaner and happier. Last year she was featured in the plant-based athletes documentary The Game Changers and said, “Being vegan has helped me immensely. I don’t feel sluggish like I did when I was eating meat, and my recovery from training really took off. It felt like an overall cleanse for my body, and I started seeing greater results on the track.” Now Michelle is committed for the planet as well. “Ultimately helping the environment and not contributing to animal cruelty was a big thing for me, too. That was my initial reason for going vegan, and the rest of the benefits were just added bonuses.” Mitchell describes what she eats in a day for enhanced performance and more energy to win sprints. “I like to make sure I have three different types of protein in there. I use tofu, beans, and mushrooms, along with spinach, vegan cheese, and hash browns,” she says. “I also love to add Beyond Meat for more flavor, which is a great source of plant protein as well. That usually keeps me full for the better part of the day," she told Well + Good.
11. Lewis Hamilton: Formula One Driver Who Credits His Vegan Diet For Allowing Him to Be Victorious
"We were taught that eating animal products was good for us but we've been lied to for hundreds of years," said Lewis Hamilton. The Beet reported on Hamiltion's vegan diet quoting The New York Times that he credits his new plant-based diet with making the difference in his career. Hamilton gave up processed food and animal products for vegetables, fruit, nuts, grains, because of his strong compassion for animals, for the benefit of the environment, and his own health. Hamilton isn't the only vegan in his family. His dog Rocco is fully vegan and Hamilton says he's "super happy" on Rocco's very own IG post. Earlier this year, Hamilton gave up his private jet because he said it's a big pollutant and aims to live a sustainable lifestyle. Back in February, he started a line of sustainable clothing with Tommy Hilfiger at London Fashion Week.
12. Patrik Baboumian: Arguably The Strongest Man in The World
Featured in The Game Changers for his elite strength and his superhuman ability to lift a car, Patrik Baboumiam is one of the strongest men in the world and also happens to be vegan. Baboumian lifted 358 pounds in the 2009 German log lift nationals. Back in 2014, Baboumiam partnered with PETA in his campaign "Want to be Stronger" describing powering yourself with plants and how you can build muscle without eating meat. One of his 2019 PETA campaigns showed him posing with crossed arms and leaves in his mouths with the text: "The world's strongest animals are plant-eaters: Gorillas, buffaloes, elephants and me." Bahoumiam's diet consists of a dairy-free shake for breakfast with 8 grams of protein and 0 carbohydrates. For lunch, he enjoys vegan sausage, falafel, low-fat oven fires, peppers, and more grilled veggies. He normally eats 250 grams of carbs and 90 grams of protein just for lunch. Dinner includes vegetables cooked potatoes, and tofu. If you want to eat like Boubanian, he reports his food diary on his blog BarBend.
13. Arnold Schwarzenegger: Former Proessional BodyBuilder, Producer, The Game Changers, and former Governor of California
Here's a guy who has worn many hats: Bodybuilder, Terminator, California Governor, and now vegan and advocate for the plant-based lifestyle. Arnold Schwarzenegger ditched meat and dairy and has proven that you don't need to eat animal products to be strong, healthy and reverse symptoms of heart disease. Now 73, he had a pulmonary valve replacement 1997 due to a congenital defect and underwent emergency open-heart surgery in 2018 to replace the valve again. He then changed his eating and fitness habits and now extolls the virtues of plant-based eating for the environment as well as health reasons. He is a producer of The Game Changers (a movie with many masters) and an advocate for going vegan for health, the environment and the sake of animals (he posts on IG with his pet donkey and miniature pony, both household dwelling animals). Schwarzenegger said last year: "Right now, seven million people are dying every year. That is alarming and everyone in the government has the responsibility to protect the people.... 28 percent of the greenhouse gasses come from eating meat and from raising cattle, so we can do a much better job."
14. Scott Jurek: Named One of The Greatest Ultra-Marathoner's Of All Time Read More: 20 Who Athletes Swear by a Plant-Based Diet to Boost Performance
Jurek is an extreme ultra-marathon runner who has won the Hardrock Hundred, the Badwater Ultramarathon, the Spartathlon, and the Western States 100 Mile Endurance Run (you get the idea). Jurek has been vegan for almost two decades, after easing into it by cutting out meat in college, he slowly stopping seafood and finally giving up all animal products once he realized that eating this way made him feel healthier and happier. To run such an extreme amount of miles, you need to fuel your body with plant-based foods that will give you enough energy and carbohydrates to go the distance. The goal is to eat 5,000-6,000 calories of plant-based foods daily. Jurek outlined his plant-based diet in an interview with Bon Appetite. Instead of waking up to a hot cup of coffee to boost energy, he prefers to drink tea and a green smoothie with spirulina or chlorella and a host of other ingredients. He adds bananas, frozen pineapple slices, or mangoes, brown rice and pea protein, (for protein) to rebuild what's lost in training. This is not just any smoothie.
15. Alex Morgan: USA Soccer Star, Plays for the Orlando Pride of the NWSL
Soccer star, Alex Morgan is one of the beloved members of the USA National Team that won the World Cup and has shown that the female players deserve to get equal pay as their male counterparts by the US Soccer Federation. She is also an animal rights advocate and longtime vegan, having given up meat when she decided that "it didn't feel fair to have a dog, and yet eat meat all the time,” referring to her adorable pup Blue. Morgan aims to eat 90 grams of plant-based protein daily to stay fit and lean, especially for her workouts and on the field. Morgan admitted that breakfast was difficult because "a lot of the things I love like pancakes and French toast had dairy and eggs." But now she enjoys oatmeal with nut butter and berries, smoothies, rice, quinoa, veggies, black beans, protein shakes, Mediterranean food, Impossible burgers, Mexican beans, and sauteed veggie burritos, she told USA Today.
16. Paul Rabil: Pro Lacrosse Player: A Vegan Diet Helped Alleviate His Sciatica
Paul Rabil who played for the Boston Cannons and the New York Lizards of Major League Lacrosse, ditched meat and dairy after his 2019 season ended and revealed he's now "officially" vegan on YouTube. "At first [switching to a plant-based diet] was to help solve some pain and trauma that I was going through. Over the last two years, I've had two herniated discs.... and that has led to a ton of shooting pain down my legs, its called sciatica," Rabil explains the purpose of his diet switch. He adds: "I've tried to a lot of things; I've had a number of cortisone shots; I've done physical therapy for two years. And I reached a place where I was thinking 'okay maybe I can solve this with nutrition because a lot of our pain stems from inflammation. Within a few weeks, I started noticing a lot of alleviation so I started focusing and doubling down more on veganism"
17. Hannah Teter: 2006 Olympic Snowboard Gold Medalist
Hannah Teter won Olympic gold and silver in the halfpipe and is also a seven-time XGames medalist. She changed her diet after watching the documentary, Earthlings when she discovered how "horrible" factory farming is. After a strict vegetarian diet, Teter liked the way she performed and believes that her diet helped her win gold at the 2006 games. She now considers herself "plant-based" and in an interview with the Huffington Post, Teter said, "I feel stronger than I’ve ever been, mentally, physically, and emotionally. My plant-based diet has opened up more doors to being an athlete. It’s a whole other level that I’m elevating to. I stopped eating animals about a year ago, and it’s a new life. I feel like a new person, a new athlete."
18. Nick Kyrgios: Professional Tennis Champion Ranked 40 in The World
Djokovic is not the only tour player to go plant-based. Nick Kyrgios shared that he does not eat meat anymore because of his strong compassion for animals. During the time of the Australian wildfires, the Aussie native explained: "I've been passionate about animal welfare for some time now. I don't eat meat or dairy anymore. That’s not for my health, I just don’t believe in eating animals." "I tried a vegan diet a couple of years ago but with all the travel I do, it was hard to stick to it. Since then I've managed to make it work, and I've been vegetarian for quite a while. "Seeing the footage of these animals suffering from the fires only reinforces why I've chosen this diet. When I see these terrible photos, I can’t comprehend eating meat."
19. Matt Frazier: Ultra-Marathoner Credits Vegan Diet For Breaking Personal Records
Matt Frazier has run 27 ultra-marathons in his career so far and continues to write about the endurance strength of being a vegan athlete in his personal blog, which he started 11 years ago: No Meat Athlete. The Beet recently interviewed Frazier about his vegan journey and how to be a successful athlete on a plant-based diet. When asked about the first time he ditched meat Frazier replied, "I had already cut 90 minutes off my first marathon time. I was still 10 minutes away from the Boston Marathon qualifying time. I had plateaued, and I was not sure how I was going to find 10 minutes. [Plant-based eating] was what I was missing. That’s what it took. The other big noticeable difference to me [after going vegan] was I stopped getting injured. Injuries had always been a big part of my running journey. When I became vegan, it was around the time I ran three 50-milers and a 100-miler. I didn’t have any injuries. If it’s done right, [plant-based diets] can really help you recover faster."
20. Michaela Copenhaver: Professional Rower, World Record Holder, 10,000m Indoor
Rowing is grueling. It's known as the toughest endurance sport in the world. The world record-breaking female rower, Michaela Copenhaver went vegan in 2012 for ethical reasons, she told Great Vegan Athletes. “Initially, I just wanted to eat more vegetables. Those things are super good for you, and they're delicious. Being vegetarian and vegan made me more conscious of how many servings I was getting a day (or not).” When she switched from vegetarian to vegan it was almost accidental: “I was traveling for a regatta in the fall of 2012. I had been vegetarian for 1.5 years already but relied pretty heavily on dairy and eggs. While I was traveling, I was bouncing from couch to couch and had no way to safely store dairy or eggs—so I decided to try a week without them. I felt great, and it wasn’t nearly as scary as I thought. I’ve been vegan ever since.” Now it's a value system: “Once I stopped eating and using animals, I felt I could finally address a question that had been bothering me for a long time—what right do we have to exploit other creatures? Now, I understand that we have no right, and my motivations are primarily ethical.”
More From The Beet