Study: To Lower Risk of Serious Disease, Choose Plant-Based Sources of Protein
Americans are obsessed with protein, even though research tells us we don't need to be. There is no shortage of protein in the standard American diet and protein deficiency is almost unheard of in this country. Yet a new study further clarifies that rather than worry about how much protein we are getting, we should be concerned with the source of our protein. Eat more plant-based protein and you reduce the risk of disease and premature mortality.
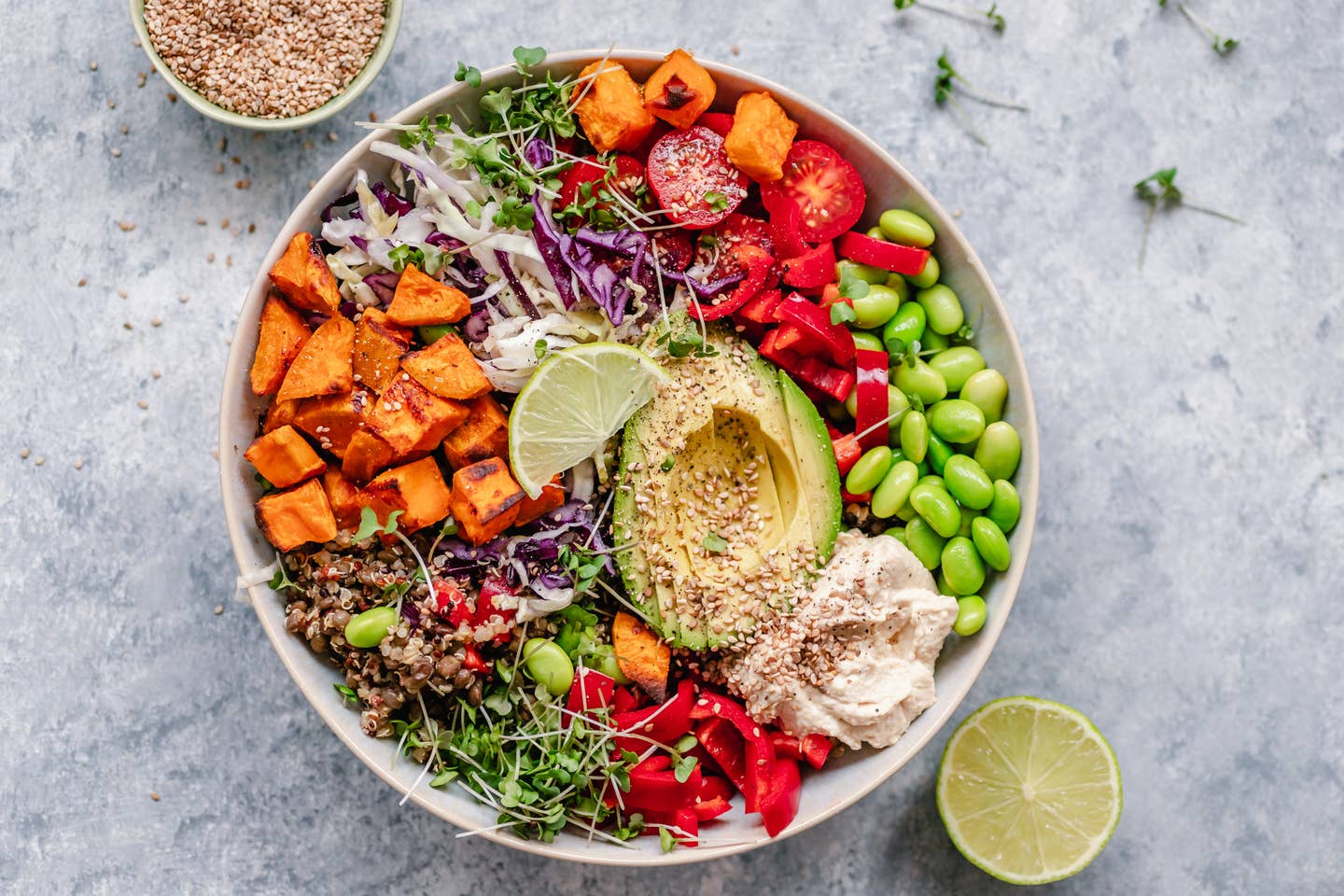
Titled “Association of Major Dietary Protein Sources With All‐Cause and Cause‐Specific Mortality: Prospective Cohort Study,” the study comes down to straightforward findings: Ditch animal proteins in favor of plant-based protein from legumes, nuts, seeds, vegetables and fruit, and you’ll live a healthier, longer life. The next time someone brings up how much protein a single food has, tell them that what matters more is the source of your protein. This study tells us that if you're seeking protein, eating plant-based sources will reduce your risk of premature mortality -- of any cause.
"Different dietary protein sources have varying associations with all‐cause mortality, cardiovascular disease mortality, and dementia mortality," the study concludes. "Our findings support the need for consideration of protein sources in future dietary guidelines."
Published in the Journal of the American Heart Association in February, the longitudinal study tracked 102,521 postmenopausal women enrolled in the Women’s Health Initiative in the '90s and tracked their intake and overall health and disease rates for the next 30 years.
Swapping Animal Proteins for Plant-Based Can Help Improve Health
The data revealed that consuming plant-based protein was inversely associated with all‐cause mortality, including cardiovascular disease, dementia, and other causes of death. Whereas eating animal protein was associated with enhanced mortality risk on a variety of fronts.
“Among major protein sources, comparing the highest with the lowest [amount] of consumption, processed red meat or eggs was associated with a higher risk of all‐cause mortality," the study found. "Unprocessed red meat, eggs, or dairy products, were associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease mortality.”
The researchers also found that egg consumption was associated with a higher risk of cancer deaths, whereas consumption of processed red meat (such as bacon, sausage, hot dogs, ham and bologna, and the like) was associated with a higher risk of dementia death.
When considering their findings in a manner referred to as substitution analysis, scientists found that substituting plant protein for animal protein was associated with a lower risk of all‐cause mortality, cardiovascular disease mortality, and dementia mortality, and substitution of total red meat, eggs, or dairy products with nuts was associated with a lower risk of all‐cause mortality.
How to Use This Research to Improve Your Own Diet
So what do nutritionists make of these findings? Eat more plant-based, whole-foods and you get all the protein you need, from sources that are healthier for you than animal sources. “This study is very interesting and highlights the fact that we should all be eating more plant proteins and less processed red meat since the study, found that eating more plant proteins may lower your risk of death from heart disease and dementia,” comments Amy Gorin, MS, RDN, a plant-based registered dietitian and owner of Plant-Based Eats in Stamford, Connecticut (Gorin was not associated with the research).
Nutritionist Jinan Banna, Ph.D., RD, adds, “We know that plant sources of protein provide important nutrients that animal sources don't, such as particular antioxidants. These findings add to a body of evidence on the potential benefits of emphasizing plant-based foods in the diet for health,” noting that additional research regarding protein sources and health is needed.
“When it comes to adding more plant protein to your plate, I suggest adding in a variety of sources such as tofu, edamame, pulses, nuts, seeds, and quinoa,” she continues, adding that you can also sneak in plant protein from desserts, as in her chickpea chocolate cookie dough. We’ll never turn down the chance to eat more cookie dough. Catch you on the plant-side.
The Top 20 Veggies with the Most Protein
1. Soy Beans
Soybeans are a legume but they are such a great source of protein that we had to lead the veggie list with it. There is more protein in just one ounce of soybeans than a cup of sliced avocado! 1 cup equals Protein - 28.6g Calories - 298 Carbs - 17.1g Fiber - 10.3g Calcium - 175mg
2. Peas
If the pod, that peas are grown in, is split down the middle, that is an indicator they are ripe. Seeds inside the pod vary and can be green, white or yellow. 1 cup equals Protein - 8.6g Calories - 134 Carbs - 25g Fiber - 8.8g Calcium - 43.2 mg
3. Corn
Fresh corn is a great source of energy for those who like to stay active. Protein isn't all that corn has to offer. Corn provides the body with potassium and B vitamins. 1 cup equals Protein - 5.4g Calories - 177 Carbs - 123g Fiber - 4.6g Calcium - 4.9mg
4. Artichoke Hearts
Artichokes are part of the sunflower family. The fiber in artichoke hearts is great for supporting digestion. 1 cup equals Protein - 4.8g Calories - 89 Carbs - 20g Fiber - 14.4g Calcium - 35.2mg
5. Asparagus
If not properly stored, Asparagus tends to go bad quickly, To elongate freshness, put damp paper towels around the stems, or place the entire asparagus bunch in a cup of water (like flowers) to maintain freshness longer. 1 cup equals Protein - 4.4g Calories - 39.6 Carbs - 7.4g Fiber - 3.6g Calcium - 41.4mg
6. Brussel Sprouts
Brussel sprouts have more Vitamin C than an orange. If your Brussel sprouts have a rancid odor that is an indicator you overcooked them. The smell occurs because the sprouts are composed of a great amount of sulforaphane. 1 cup equals Protein - 4g Calories - 56.2 Carbs - 40g Fiber - 4g Calcium - 56.2mg
7. Broccoli
If you are trying to lose weight broccoli is a great addition to your diet because it consists of 90 water and is also high in fiber. 1 cup (chopped) equals Protein - 3.8g Calories - 54.6Carbs - 11.2g Fiber - 5.2g Calcium - 62.4mg
8. Mustard Greens
Mustard greens provide the body with tons of Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin K and fiber. Adding steamed mustard greens into your diet has been known to lower cholesterol and reduce inflammation. 1 cup equals Protein - 3.2 g Calories - 21 Carbs - 2.9g Fiber - 2.8g Calcium - 104mg
9. Avocado
Avocado is commonly mistaken as a vegetable but it is technically a fruit. This fruit had to be included in our veggie list because it isn't just tasty but super nutritious. Avocados are packed with protein but they are a great source of potassium and fiber. Avocados are a great addition to any salad, sandwich and even smoothie! 1 cup equals Protein - 3.0 g Calories - 240 Carbs - 12.8 g Fiber - 10.1g Calcium - 18 mg
Onions are an unappreciated food hero since they provide 20 percent of your daily Vitamin C and deliver an abundance of antioxidants that can reduce inflammation. 1 cup (chopped) equals Protein - 2.9g Calories - 92.4 Carbs - 21.3g Fiber - 2.9g Calcium - 46.2mg
11. Beets
The entire beetroot is edible including the leaves which contain loads of vitamin A, calcium, iron and potassium. Beetroot is high in sugar but is considered one of the most nutritious veggies used in salads and soups. 1 cup equals Protein - 2.8 g Calories - 74.8 Carbs - 17g Fiber - 3.4g Calcium - 27.2mg
12. Oyster Mushrooms
Oyster mushrooms are commonly seen in Chinese dishes. They grow best in a controlled environment indoors. Oyster mushrooms have so many nutrients to offer besides protein such as iron, calcium, zinc and folic acid. 1 cup (raw and sliced) equals Protein - 2.8g Calories - 37 Carbs - 5.6g Fiber - 2.0g Calcium - 2.6mg
13. Bok Choy
Bok Choy is a member of the mustard family. One of the oldest cultivated vegetables in the world, Bok Choy means "white vegetable” and is a great source of vitamins A, C, B6, K, and E, magnesium, potassium, iron, manganese, and calcium. 1 cup equals Protein - 2.7 g Calories - 20.4 Carbs - 3.1g Fiber - 1.7g Calcium - 158mg
14. Green Beans
Green beans are a great source of vitamins B, C and K, and minerals such as magnesium, iron and manganese. Green beans should be cooked before eating, to destroy lectins. China is the biggest grower of green beans in the world, exporting over 15 million tons a year. 1 cup equals Protein - 1.8 g Calories - 31 Carbs - 7 g Fiber - 2.7 g Calcium - 37 mg
15. Cauliflower
The most nutritious way to consume cauliflower is steamed. Don't get intimidated by orange, purple or green cauliflower. All three types have the same benefits as white cauliflower. 1 cup equals Protein - 2.2g Calories - 28.6 Carbs - 5.4g Fiber - 2.8g Calcium - 19.8mg
16. Turnip
You can eat the entire plant, root and leaves. The turnip root is high in vitamin C and the greens are high in vitamins A, C, E, B6 and K, believed to counter inflammation. Add turnip roots to soup, or mash them. Add them to salads. 1 cup equals Protein - 1.6g Calories - 28.8 Carbs - 6.3g Fiber - 5.0g Calcium - 197mg
17. Alfalfa Sprouts
Alfalfa sprouts might be little but they sure are powerful. Plus they're quick and easy to grow. They are loaded with Vitamin C, Vitamin K, Iron and more. But because they have been known to carry bacteria, make sure to fully cook alfalfa sprouts if you have a fragile immune system or are pregnant. 1 cup equals Protein - 1.3 g Calories - 8 Carbs - 0.7 g Fiber - 0.6 g Calcium - 10.6 mg
18. Tomatoes
Keep your tomatoes fresher for longer by storing them stem down. When exposed to sunlight the Vitamin C in a tomato will diminish. 1 cup equals Protein - 1.3g Calories - 26.8 Carbs - 5.8g Fiber - 1.8g Calcium - 14.9mg
19. Zucchini
Zucchini has an abundance of potassium, even more than a banana! The reason zucchini isn't high in calories is that it is made up of 95% water. 1 cup equals Protein - 1.2g Calories - 28.8 Carbs - 7.1g Fiber - 2.5g Calcium - 23.4 mg
20. Spinach
Spinach is filled with Vitamin A, Vitamin E, Vitamin K, fiber and protein. The best part about spinach is you can sauté it, blend it or eat it raw! Spinach is best grown in rainy and cool weather. 1 cup equals Protein - 0.9g Calories - 6.4 Carbs - 1.0 g Fiber - 0.6g Calcium - 27.7 mg
Top 15 Legumes and Beans
1. Soy Beans
Soybeans are a legume but they are such a great source of protein that we had to lead the veggie list with it. There is more protein in just one ounce of soybeans than a cup of sliced avocado! 1 cup equals Protein - 28.6g Calories - 298 Carbs - 17.1g Fiber - 10.3g Calcium - 175mg
2. Lentils
Lentils are the only beans that don't have to be soaked before preparing. Lentils can be the star of any dish that needs heft, from soups to burgers. Next time it's Taco Tuesday, try out lentil tacos—they pack a protein punch. 1 cup equals Protein - 17.9 g Calories - 230 Carbs - 39.9 g Fiber - 15.6 g Calcium - 37.6 mg
3. White Beans
Dried white beans can be stored for up to three years in a dry, room-temperature location. Which means you can keep them around whenever you need a staple for soups or stews. 1 cup equals Protein - 17.4 g Calories - 249 Carbs - 44.9 g Fiber -11.3 g Calcium - 161 mg
4. Edamame
Edamame is a great snack to keep in your freezer. Microwave them and spice them up with a sprinkle of salt, chili powder and red pepper flakes. You'll be enjoying a protein-filled snack that is better than chips. 1 cup (cooked and shelled) equals Protein - 16.9 g Calories - 189 Carbs - 15.8g Fiber - 8.1g Calcium - 97.6mg
5. Cranberry Beans
As you cook cranberry beans, the unique specks of red that give these legumes their name vanish. Boil the cranberry beans, blend into a spread and use as a delicious dip with veggies for a great protein snack. 1 cup equals Protein - 16.5 g Calories - 241 Carbs - 43.3 g Fiber - 15.2 g Calcium - 88.5 mg
6. Split Peas
Don't confuse split peas with green peas. Split peas are dried and—surprise— split. Unlike their sweet cousins, these peas must be boiled for 45 minutes before they're ready to eat. Make Ina Garten's easy Parker's Split Pea Soup for a protein-packed lunch. 1 cup cooked Protein - 16.3 g Calories - 229 Carbs - 41.1 g Fiber - 16.3 g Calcium - 27.4 mg
7. Kidney Beans
Make sure to soak these beans overnight to get rid of the toxic proteins in the raw bean that is harmful to people and animals. then cook thoroughly before eating. Soaking and cooking the beans will get rid of the harmful proteins. Then, dig in! 1 cup equals Protein - 15.3 g Calories - 225 Carbs - 40.4 g Fiber - 13.1 g Calcium - 49.6 mg
8. Black Beans
Black "turtle" bean is the technical name for this crowd favorite. The "turtle" part comes from the physical appearance of the shiny exterior shell that protects the bean. 1 cup equals Protein - 15.2 g Calories - 227 Carbs - 40.8 g Fiber - 15 g Calcium - 46.4 mg
9. Navy Beans
As you can see, navy beans are clearly not navy. So where did the name come from? These beans were such an important part of the U.S. Navy diet in the beginning of the 20th century that the beans were named after them. Anchors aweigh! 1 cup equals Protein - 15 g Calories - 255 Carbs - 47.4 g Calcium - 126 mg
10. Pinto Beans
Canned pinto beans aren't just a source of protein, but also major fiber. Pinto beans are often used as refried beans because they fall apart when steamed. 1 cup equals Protein - 15.4g Calories - 245 Carbs - 44.8g Fiber - 15.4g Calcium - 78.6mg
11. Chickpeas
What's better than hummus for boosting protein? Not much. Just half a cup delivers 10 grams of protein, which is a good percentage of your daily needs: ranging from 45 to 65 grams, depending on weight, gender and activity level. 1 cup equals Protein - 14.5g Calories - 269 Carbs - 45g Fiber - 12.5 g Calcium - 80.4 mg
12. Lima Beans
Lima beans are often called "butter beans" because of their buttery taste. Famously used in succotash, lima beans can also be used boost the taste of a hearty vegetable soup, or roast them with sweet potatoes as a side dish. 1 cup equals Protein - 14.7 g Calories - 216 Carbs - 39.3g Fiber - 13.2g Calcium - 32mg
13. Mung Beans
Mung beans lack a lot of flavor but are great to add to any dish for crunch and protein. Trade your chickpea-based falafel for a mung bean option to switch things up. Fact: Just Eggs uses mung beans for protein! 1 cup equals Protein - 14.2 g Calories - 212 Carbs - 38.7 g Fiber - 15.4 g Calcium - 54.5 mg
14. Fava Beans
Take the fava beans out of the pod since experts don't recommend eating that part. For freshest taste, only separate the beans from the pods when you 're ready to eat them. 1 cup equals Protein - 12.9 g Calories - 185 Carbs - 33.2 g Fiber - 9.18 g Calcium - 61.2 mg
15. Peas
Who knew little old peas pack a major protein punch? One cup of peas has more protein than one average-sized egg. Yep, you can make a bet and win it. 1 cup equals Protein - 8.6g Calories - 134 Carbs - 25g Fiber - 8.8 g Calcium - 43.2 mg
11 Nuts With the Most Protein
1. Peanuts
Peanuts are actually not nuts—they're legumes which grow underground, so they are in the same family as chickpeas, soybeans and lentils. Crazy stunt: Scientists have made diamonds out of peanuts by putting them under enormous pressure. 1 ounce equals Protein - 7.31 g Calories - 161 Carbs - 4.57 g Fiber - 2.41 g Calcium - 26.1 mg
2. Almonds
Almonds are part of the cherry, peach, and mango family, since they are a drupe (a fleshy fruit with skin thin and central seed). When you eat a peach or mango, notice how the pit looks similar to an almond. There are over 30 different varieties and eight out of 10 almonds are grown in California. It takes over 1 gallon of water to produce a single almond, or 1900 gallons to grow 1 pound. 1 ounce equals Protein - 6g Calories - 164 Carbs - 6.11g Fiber - 3.5 g Calcium - 76.3mg
3. Pistachios
Pistachios are one of the oldest nut trees in the world. Humans ate pistachios as early as 7,000 B.C. They spread across the Middle East to the Mediterranean and were viewed as a royal delicacy. 1 ounce equals Protein - 5.72 g Calories - 159 Carbs - 7.7 g Fiber - 3 g Calcium - 29.8 mg
4. Cashews
Get ready, because November 23rd is National Cashew Day! The U.S eats over 90% of the world’s cashews. These tree nuts start out as apples. Harvesters then take the seed from the bottom of the apple and before the seed is roasted, it is usually green. Roasting or steaming the cashew neutralizes the oils and makes them safe to eat—meaning raw cashews aren't *truly* raw. 1 ounce equals Protein - 5.16 g Calories - 157 Carbs - 8.56 g Fiber - 0.936 g Calcium - 10.5 mg
5. Walnuts
Walnuts contain more Omega-3 fatty acids than any other nut, so they are an excellent brain food to boost memory (they even look like little brains!). To keep them fresher longer, store walnuts in the fridge or freezer, since they have a tendency to go rancid quickly. 1 ounce equals Protein - 4.32g Calories - 185 Carbs - 3.89g Fiber - 1.9g Calcium - 27.8mg
6. Hazelnuts
Hazelnuts contain healthy doses of fiber, folate and vitamin E. Hazelnut oil is so rich it's used in combination with palm oil for cleaning and polishing wood. We love them with dark chocolate. 1 ounce equals Protein - 4.24 g Calories - 178 Carbs - 4.73 g Fiber - 2.75 g Calcium - 32.3 mg
7. Brazil Nuts
It is illegal to cut down a Brazil nut tree, which live for up to 500 years. These are like the candy of the nut family since a cup has 876 calories, and each nut is 85% fat and 14% protein. They're rich in selenium, a mineral prized for thyroid support. 1 ounce equals Protein - 4.06 g Calories - 187 Carbs - 3.33 g Fiber - 2.13 g Calcium - 45.4 mg
8. Pine Nuts
Pine nut is another type of seed that is clumped in with the nuts. They are so expensive because they are tedious to gather. They grow in the pine cone, but you generally can't consume pine nuts from a pine cone you'd find in your park or backyard as not all pine nuts are edible. Most of the pine nuts you eat come from the stone pine tree in Asia, Europe and North America. 1 ounce equals Protein - 3.88 g Calories - 191 Carbs - 3.71 g Fiber - 1.05 g Calcium - 4.54 mg
9. Pecans
French people who settled in New Orleans created the first pecan pie, since pecans are native to the southern US. On average, 78 pecans are used in one pie. There are over 1,000 varieties of pecans, and many are named after Native American tribes. 1 ounce equals Protein - 2.6g Calories - 196 Carbs - 3.93 g Fiber - 2.72 g Calcium - 19.8 mg
10. Macadamia Nuts
Macadamia nuts are actually seeds. It takes 12-15 years for a macadamia tree to grow to its full size. Most of the world’s macadamia nuts come from Hawaii. They are high in carbs and protein, but keep these nuts away from dogs since they make them sick. 1 ounce equals Protein - 2.24 g Calories - 204 Carbs - 3.92 g Fiber - 2.44 g Calcium - 24.1 mg
11. Chestnuts
Chestnuts are the only nut that contains vitamin C. The trees were hit by blight in the nineties and 3 billion trees were eventually wiped out. Chestnuts are used in beer and cake and eaten creamed around the holidays. Chestnut flour is gluten-free, making it a great alternative for cookies, pies and stuffing. 1 ounce equals Protein - 1.19g Calories - 63.5 Carbs - 13.9g Calcium - 5.1mg
More From The Beet